Computed Radiography for Cross-Country Pipelines
- Rohit Bafna
- Oct 16, 2024
- 3 min read
Updated: Nov 10, 2024
TCR Engineering, with its expertise in Computed Radiography (CR), is committed to providing reliable and high-quality NDT services, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of cross-country pipelines for industries around the world.
Shown in this video, is a TCR technician demonstrating how he undertakes CR at a project site in India.
Computed Radiography (CR) is an advanced form of radiographic inspection that uses imaging plates (IP) instead of traditional X-ray films to capture images of pipeline welds. These plates, coated with phosphor, store the radiographic image when exposed to X-rays or gamma rays. The stored image is then read by a laser scanner and converted into a digital image, which can be viewed, analyzed, and archived electronically.
Advantages of Computed Radiography over Conventional RT
a. Higher Image Quality and Accuracy
Sharper Image Resolution: CR provides high-resolution digital images that offer better contrast and sharpness than conventional film radiography. This improves the ability to detect fine defects, such as small cracks, inclusions, porosity, and undercutting in the welds of cross-country pipelines.
Real-Time Image Analysis: The digital nature of CR allows for real-time image processing and enhancement, helping inspectors zoom in, adjust contrast, and perform detailed analyses without waiting for films to develop.
b. Faster Turnaround Time
Quick Scanning and Processing: The entire process of image capture, scanning, and processing in CR is significantly faster compared to the time-consuming steps involved in film development in conventional RT.
Immediate Feedback: Inspectors can quickly identify defects in welds and take corrective actions on-site, reducing downtime and minimizing delays in pipeline construction or maintenance.
c. Cost-Effectiveness
Reduced Consumables: CR eliminates the need for costly radiographic films, chemicals, and darkroom equipment required for film processing in conventional RT. This reduction in consumable costs leads to significant savings over time.
Less Storage Space: Since CR produces digital images, there is no need for physical storage of films. Digital images can be stored and archived electronically, reducing the need for bulky storage facilities and minimizing the risk of losing or damaging films.
d. Environmental and Safety Benefits
Chemical-Free: Unlike conventional RT, which requires harmful chemicals for film development, CR is a more environmentally friendly option as it eliminates the need for film processing chemicals and water waste.
Reduced Radiation Exposure: With the higher sensitivity of imaging plates in CR, lower radiation doses can be used, resulting in reduced radiation exposure for both inspectors and surrounding personnel, especially important for pipeline projects in populated areas or sensitive environments.
e. Enhanced Data Management and Archiving
Digital Storage: The digital images produced by CR can be easily stored, archived, and retrieved for future reference, providing long-term benefits for pipeline operators. Digital records can be securely shared with stakeholders or regulatory authorities as needed.
Advanced Analysis Tools: Digital radiography enables the use of advanced image analysis software, allowing inspectors to perform automated defect recognition (ADR) and other sophisticated analyses, improving the reliability of inspection results.
f. Improved Field Operation Flexibility
Portable and Lightweight Equipment: CR systems are typically more compact and portable compared to the heavy equipment used in conventional RT. This makes CR ideal for use in remote and difficult-to-access areas where cross-country pipelines are often located.
Less Maintenance: Since CR uses digital technology, it has fewer mechanical components and moving parts compared to traditional film-based systems. This leads to lower maintenance requirements and greater operational reliability in field conditions.
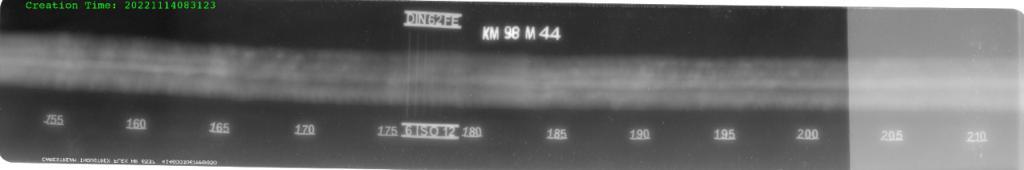
Sample images from TCR of Computed RT:
Applications in Cross-Country Pipeline Inspection
Weld Integrity Inspection: CR is widely used for inspecting welds in cross-country pipelines, providing high-resolution images that can detect a range of weld defects such as cracks, porosity, and incomplete penetration or fusion.
Corrosion Monitoring: CR is also used to monitor corrosion in pipelines, helping operators identify areas of thinning or degradation before they lead to leaks or ruptures.
Repairs and Maintenance: The ability to quickly detect defects and provide instant feedback makes CR ideal for pipeline repairs and maintenance, where speed and accuracy are critical to ensuring minimal downtime.
The adoption of Computed Radiography (CR) in the inspection of cross-country pipelines offers numerous advantages over conventional radiography testing, from improved image quality and faster turnaround times to enhanced environmental safety and cost-effectiveness. As the pipeline industry continues to prioritize both safety and efficiency, CR is quickly becoming the preferred method for ensuring the integrity of pipeline welds, making it a vital tool in the successful construction and maintenance of cross-country pipelines.